
CASE REPORT
Experience of using CAPTOR® Thrombectomy Device, EXTRAFLEX® Distal Access Catheter andSUPSELEK® Micro Catheter
AUTHOR & INSTITUTION
Dr.Wang Shouchun and Dr. Wang Chao
InterventionalNeuro-radiologists of the First Bethune Hospital of Jilin University
CASEDESCRIPTION
Li xx, male, 36 years old
Seeing doctor at 12:23 on June 21, 2021, after "found that the right limb is not working well for 4 hours and 48 minutes"
CASEHISTORY
History of present illness
lAwoken with stroke symptoms that were not present prior to falling asleep. At the next morning (05:30 on June 21) weakness on the right side of the body was discovered by his family.
lNo abnormality is seen by head CT scan. After the diagnosis of "acute cerebral infarction", the patient's symptoms gradually worsened, showing that the right limbs were unable to move, and speech was incapable, so he was transferred to our hospital.
Past history
lFamily members complained that the patient had a history of "heart disease"
lHistory of smoking for over10 years, about 10 cigarettes/day, no abstinence, opportunistic drinking;
lDenial of history
Hypertension & diabetes,
Drugs & food allergies,
Infectious diseases such as hepatitis and tuberculosis
Trauma, surgery, and blood transfusion
Family history of cerebrovascular disease.
ADMISION to HOSPITAL
lBlood pressure
119/51mmHg
lHeart rate
66beats/min
lNeurological examination
Lethargy, complete mixed aphasia, bilateral pupils are equal in circle with diameter 3.0mm, directly and indirectly sensitive to light reflection, eyes staring to the left, right nasolabial is shallow.
Muscle strength of the right and left limb is level 1 and level 5, the muscle tension of the right upper limb is increased, the tendon reflex is symmetrically elicited, and the right Babinski (+), no item is strong.
lEmergency NIHSS score
19 points : 1 point for lethargy, 3 points for aphasia, 2 points for questioning, 2 points for instruction, 2 points for gaze, 1 point for facial paralysis, 4 points for right upper limb, 4 points for right lower limb.
Pre-PROCEDURE IMAGING
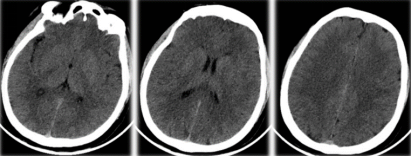
CT plain scan excluding intracranial hemorrhage, no obvious infarction was seen.
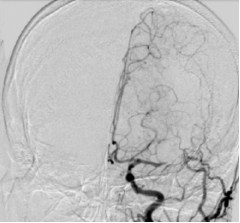
DSA Examination
The angiography of left common carotid artery confirmed that the left MCA was occluded before the bifurcation, and the ACA was slightly compensated by the pial branch, ASTIN/SIR grade 1.
The angiography of the rest cerebral artery showed no obvious abnormalities, and there was no obvious compensatory blood vessel supplying blood to the diseased area.
TREATMENT PROCESS
Preoperative Discussion
lThe patient was a young male with an acute onset and main manifestations were weakness of the right limb and speech disturbance.
lMulti-slice CT of the brain excludes hemorrhage and large-scale infarction and DSA examination shows occlusion of the left MCA
lInform family members that the patient is with intracranial occlusion, severe disability, and critical illness.
1sttreatment option is interventional cerebrovascular revascularization
2ndoption is conservative medicine treatment
Interventional treatment is currently the most cutting-edge and the most effective method of recanalizing blood vessels, with a success rate of over 90%, and a high proportion of patients returning to life independently.
However, extravasation of contrast agent, bleeding due to reperfusion, difficult recanalization and late vascular re-occlusion may occur
Conservative medical treatment have little possibility of vascular recanalization, brain tissue necrosiscontinues to progress, and may develop into large-scale cerebral infarction, symptoms aggravate and life-threatening, and late recovery effects are poor.
lFamily members agreed to undergo 1stoption of interventional treatment. By intravenous sedation, the recanalization of left MCA occlusion was performed in the emergency department.
TREATMENT DEVICES
l8F Femoral Artery Short Sheath
l8F guiding catheter
lEXTRAFLEX® SM*DAC-6S125 Distal Access Catheter
l200cm Synchro2 micro guide wire
lSUPSELEK® SM*MC-21153 Micro Catheter
lCAPTOR® 4mm×20mm HC*TDE Stent retriever
TREATMENT TECHNIQUE
lAfter the distal access catheter reached the internal carotid artery C3 section, assisted by the loath guide wire, the Synchro2 micro-guide wire carried the SUPSELEK® SM*MC-21153 micro-catheter through the EXTRAFLEX® distal access catheter.
lUnder the “road map”, the micro-guide wire carefully passed through the M1 occlusion segemnt of MCA and the micro catheter follow up to the distal end of the M2 segment.
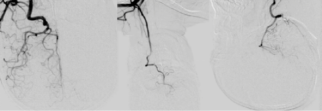
Angiography by SUPSELEK® micro catheter revealed that the MC is confirmed to be located in the true lumen of the blood vessel.
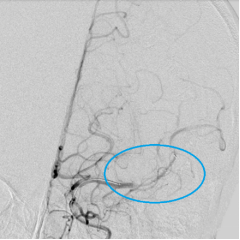
CAPTOR® 4mm×20mm HC*TDE stent retriever was delivered through SUPSELEK® micro catheter and released at the thrombus site in the left MCA.
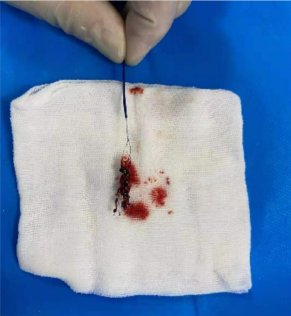
After the stent retriever stays for 5 minutes, deliver the EXTRAFLEX® distal access catheter to the proximal end of the stent retriever and slowly withdraw the stent retriever while EXTRAFLEX® distal access catheter is suctioned under negative pressure: a large dark-red thrombus can be seen with entangled the stent.
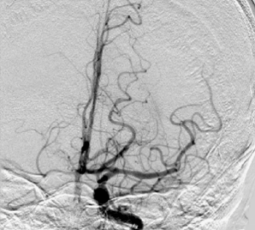
l
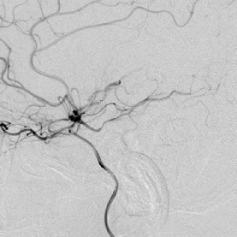
After the thrombus was removed for the 1st time, we rechecked by the 2nd angiography: the M1 of the left brain was re-canalized, the thrombus remained in the upper trunk of the middle cerebral artery, and the lower trunk was still occluded.
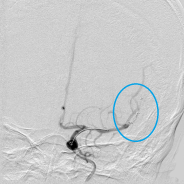
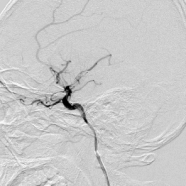
The CAPTOR® stent retriever is reintroduced through the SUPSELEK® micro catheter and released in the lower trunk of the middle cerebral artery.
l
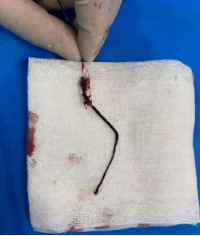
Deliver the EXTRAFLEX® distal access catheter to the proximal end of the stent retriever, and after 5 minutes, slowly withdrew the stent retriever while EXTRAFLEX® distal access catheter is suctioned under negative pressure, and a large long strip of dark-red thrombus can be seen with the stent retriever.
l
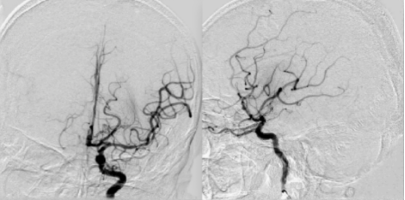
The vessel was completely re-canalized, the lumen and the blood flow was normal, the distal branches were well visualized, there was no extravasation of contrast agent, and the mTICI was grade 3.
In the last angiography of the common carotid artery, there is slight vasospasm in the C1 segment of ICA, and blood flow in the intracranial artery was smooth.
Post-PROCEDURE IMAGING
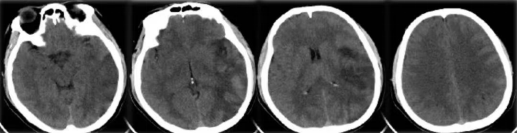
lImmediate postoperative head CT
High density of the lefttemporal parietal cortex,considering the leakage of contrast agent, excluding reperfusion hemorrhage.
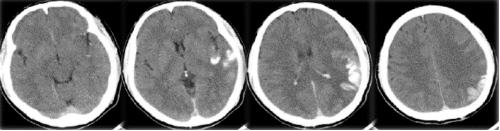
lCT 6 hours after operation
High density in the brain lobe is significantly reduced
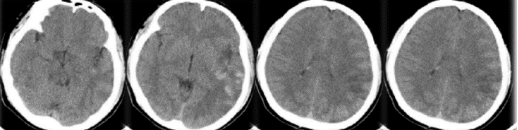
lReexamination of head CT 24 hours after surgery
No obvious reperfusion bleeding, left frontotemporal lobular infarction
Post-PROCEDURE FOLLOW-UPS
The patient’s symptoms improved significantly after the operation
lBefore operation, the patient’s right limb muscle strength is level 1 → the patient’s muscle strength returns to level 4 by 6 hours after the operation → the patient’s muscle strength returns to level 5 by 18 hours after the operation;
lThe patient has complete mixed aphasia before the operation → the patient is not complete sensory aphasia 6 hours after the procedure.
lThe patient is still in the hospital and his symptoms are gradually recovering.
CASE SUMMARY
lThis patient is 36 years old who has no chronic history of definite risk factors for cerebrovascular disease and related auxiliary examinations revealed no clear heart disease.
lEXTRAFLEX® intermediate catheter (intracranial support catheter/distal access catheter) was used in conjunction with CAPTOR® stent retriever and SUPSELEK® micro catheter, and a large thrombus were removed from the blood vessel.
lThe blood vessel was successfully re-canalized and there was no obvious abnormal change in the vascular structure.
lThe pathogenesis was considered as embolic stroke of ESUS (embolic stroke of undetermined source), and postoperative anticoagulation therapy was the first choice.
lAfter recanalization of blood vessels, the patient's symptoms improved rapidly, limb muscle strength and speech function were significantly improved, and the prognosis was good.
EXPERT REVIEWS
lHeartCare Medical CAPTOR® stent retriever with multiple segments of markers can help better visualize the position of the effective segment of the stent retriever in the blood vessel, making the positioning of the stent retriever and preliminary estimation of the thrombus length more accurate; thrombus nature and pathogenesis can be revealed by the expansion degree of the marking points.
lIn this case, with HeartCare Medical’s large-lumen EXTRAFLEX® distal access catheter, it provides better support while providing greater suction force. The patient can obtain complete recanalization after two thrombus removals, which shortens the time of interventional surgery, which is very important for patient prognosis and gained valuable time for fast recovery.